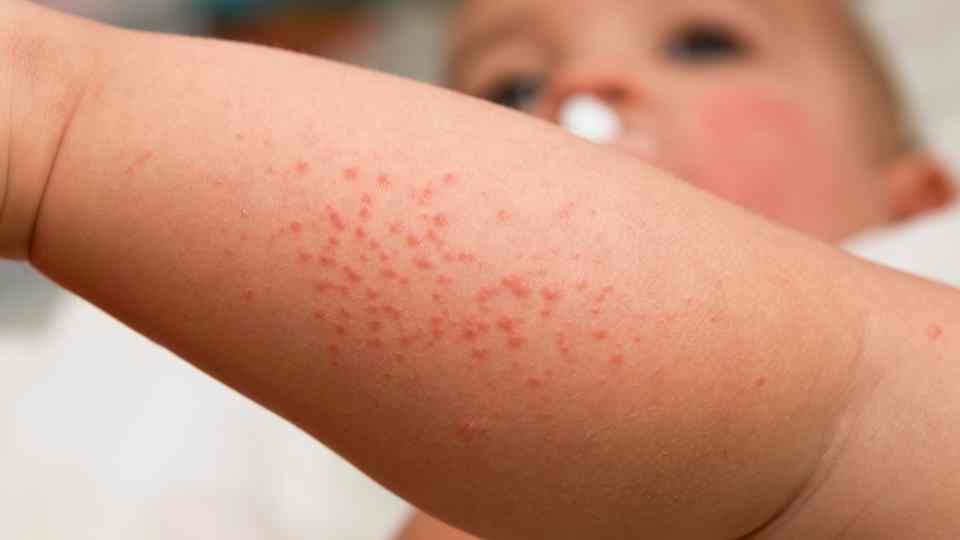
Impetigo is a common and highly contagious skin infection that primarily affects children but can occur in people of any age. Characterised by red sores and blisters, impetigo is typically caused by bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes. Despite its prevalence, impetigo is manageable with proper medical care, and can be treated by Putney Pharmacy with Pharmacy First.
Impetigo is a bacterial skin infection that leads to the formation of sores and blisters. These sores eventually burst, ooze, and form a honey-colored crust. It often begins on exposed areas of the body, such as the face, arms, or legs. Impetigo can be classified into two main types:
Other symptoms include a fever, in more severe cases, and swelling in the nearby lymph nodes, which happens as the Boyd tries to fight the infection.
Impetigo is caused by bacterial infections, primarily Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. These bacteria can enter the skin through minor cuts, insect bites, or other skin abrasions. The infection spreads easily from person to person, particularly in environments where close contact is common, such as schools, daycare centers, and sports teams.
Factors that can increase the risk of developing impetigo include:
Weakened Immune System: Individuals with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to infections.
Poor Hygiene: Inadequate handwashing and general hygiene practices can facilitate bacterial growth and spread.
Existing Skin Conditions: Conditions such as eczema or other skin injuries provide an entry point for bacteria.
Crowded Conditions: Places where people are in close contact, like schools and daycare centers, can facilitate the spread of impetigo.
A healthcare provider typically diagnoses impetigo based on the appearance of the skin and the patient’s symptoms. In some cases, a sample of the infected skin may be taken and sent to a laboratory for culture to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection. This is particularly important if the infection does not respond to initial treatments or if there is a concern about antibiotic resistance.
Treatment for impetigo usually involves a combination of topical and oral antibiotics, depending on the severity and extent of the infection:
In addition to antibiotics, general care measures include keeping the area clean, avoiding scratching, and covering the sores.
Preventing impetigo involves practicing good hygiene and taking measures to avoid spreading the infection:
While impetigo is usually manageable with treatment, there are situations where it is important to seek medical attention:
Impetigo is a common skin infection that, while often benign, requires prompt attention and appropriate treatment to prevent complications and spread. With proper care, including antibiotics and good hygiene practices, impetigo can be effectively managed and resolved. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for impetigo can help you recognise the condition early and seek appropriate care to ensure a swift recovery.

If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of impetigo, contact the Putney Pharmacy team to get an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment plan. Early intervention and adherence to treatment guidelines can help alleviate symptoms and prevent the spread of this contagious infection.